By default, Windows servers use self-signed certificates for the RDP connection. The self-signed certificates then provide a certificate warning when the RDP connection to a Windows server is established:
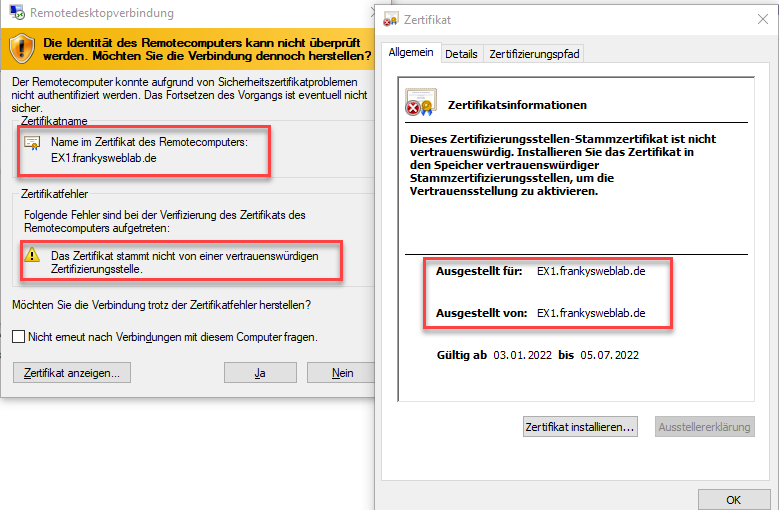
This warning can be avoided by automatically rolling out certificates from a Windows certification authority to the servers and renewing them if necessary. I have described the installation of a Windows PKI in this article described. This article is about the automatic rolling out of certificates for the RDP connection.
Create template for certificates
A new certificate template is first required so that certificates for RDP connections can be rolled out:
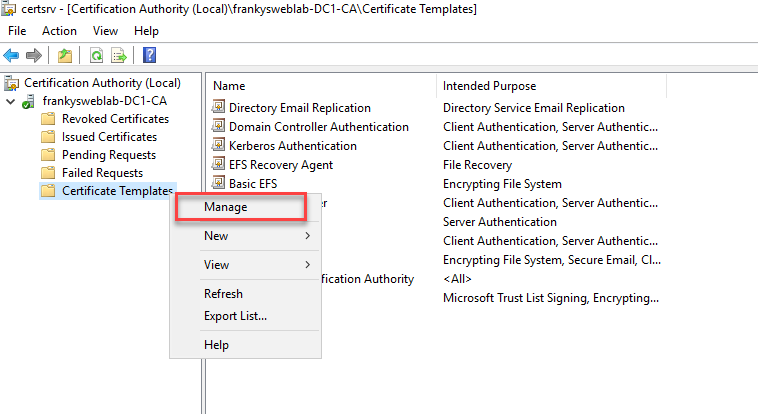
The existing template "Computer" is already quite suitable for RDP certificates and can therefore be duplicated:
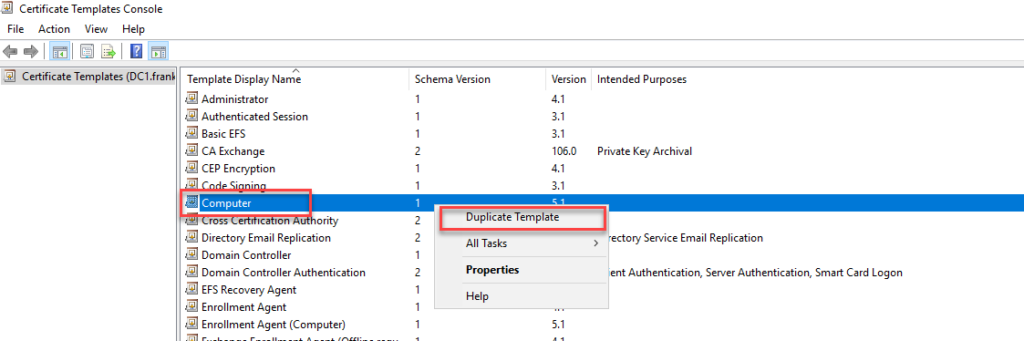
In the duplicated template, the "Application Policies" must first be edited on the "Extensions" tab:
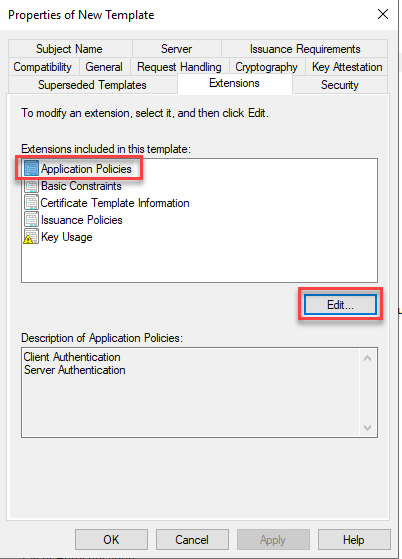
The two existing policies "Client Authentication" and "Server Authentication" are removed:
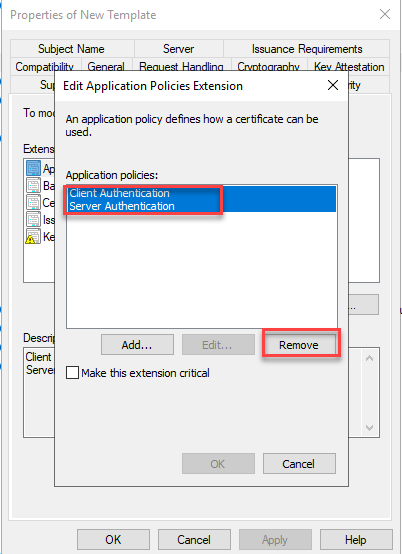
A new application policy can now be added:
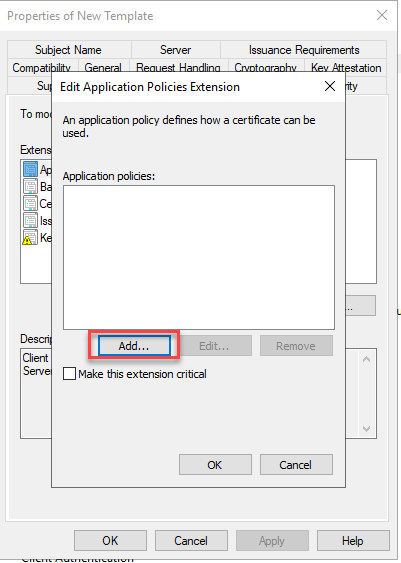
However, as there is no policy for RDP yet, this policy must first be created:
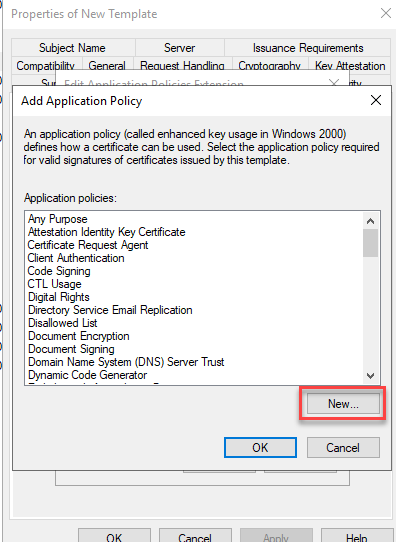
The new application policy is named "Remote Desktop Authentication" and the OID "1.3.6.1.4.1.311.54.1.2" is used as the object identifier.„ (the pre-filled OIDs are deleted):
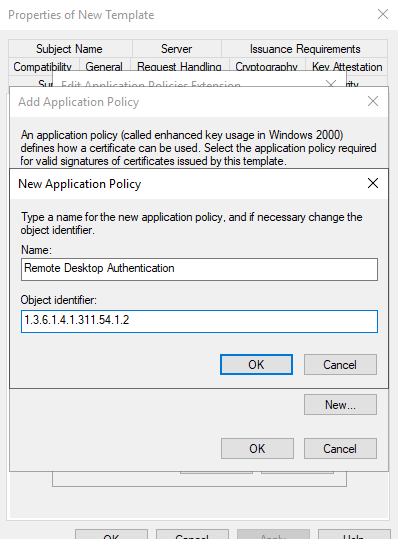
The dialogs can now be closed with OK:
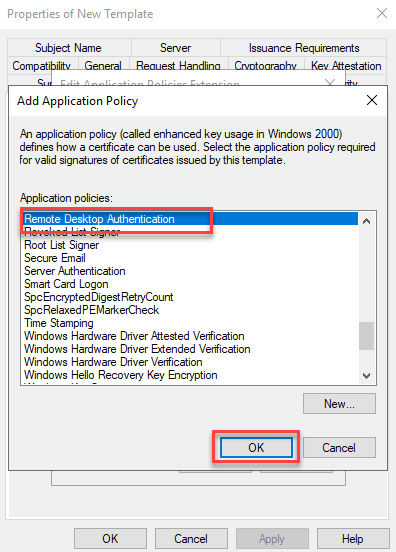
On the Security tab, the "Domain Computer" group is now given the appropriate authorizations to request the certificate:
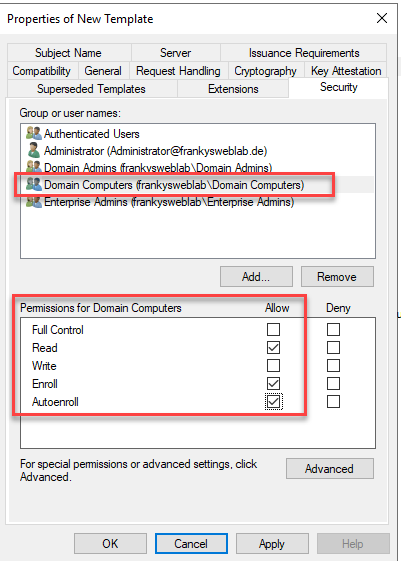
Finally, a name for the template is assigned on the General tab, in this case it is RDPCertificates. The validity can also be defined accordingly:
The dialog can be closed with OK and the new certificate template is displayed in the overview:
In order for certificates to be issued via the template, the template must be specified in the certification body as the template to be set up:
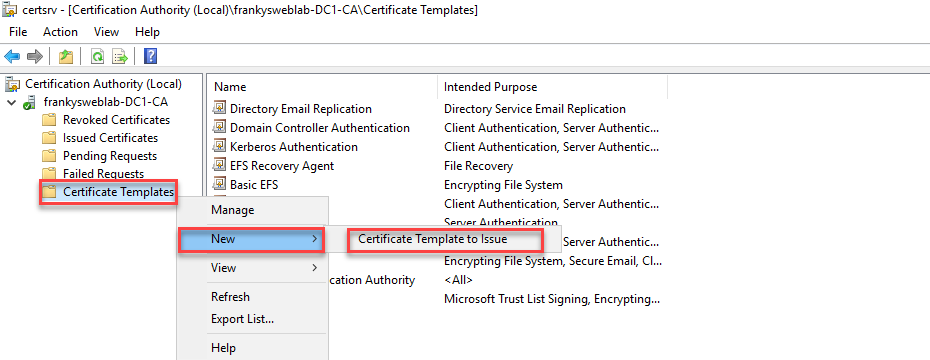
The template you have just created can be selected and added:
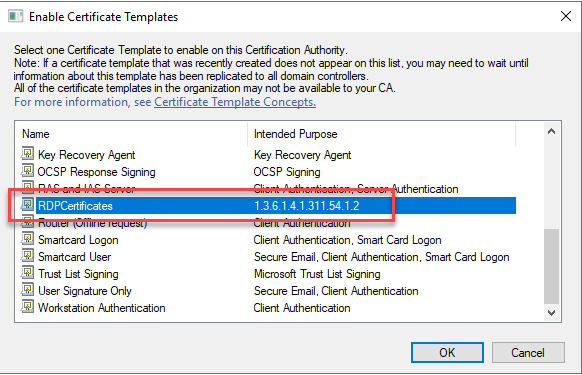
A group policy can now be created which requests the certificate and activates it for RDP connections.
Group policy for RDP certificates
A new group policy can now be created on an OU and linked directly:
The name of the group policy is freely selectable:
Under the path "Computer Configuration -> Policies -> Administrative Templates -> Windows Components -> Remote Desktop Services -> Remote Desktop Session Host -> Seurity" you will find the setting "Server authentication certificate template". This setting must be activated and the name of the previously created certificate template must be specified. In my case, this is "RDPCertificates":
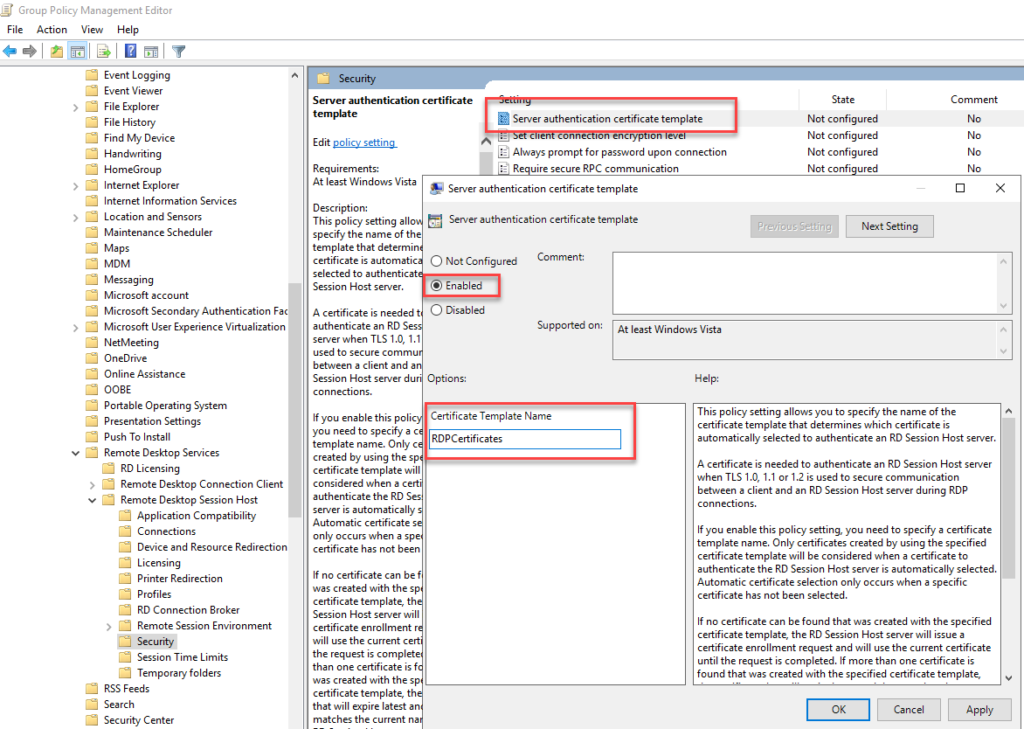
The group policy can now be linked to other OUs. As soon as the group policy is applied to the servers, a certificate is requested via the template and activated for RDP.
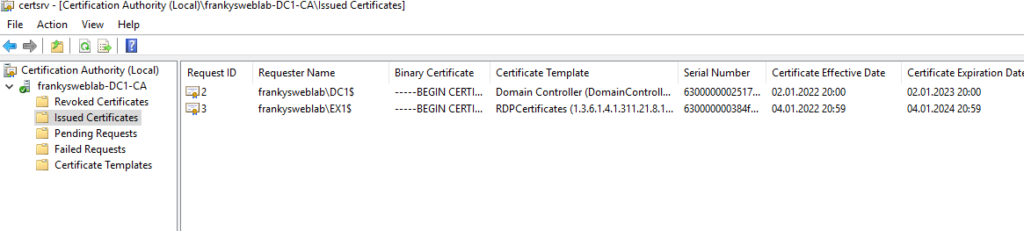
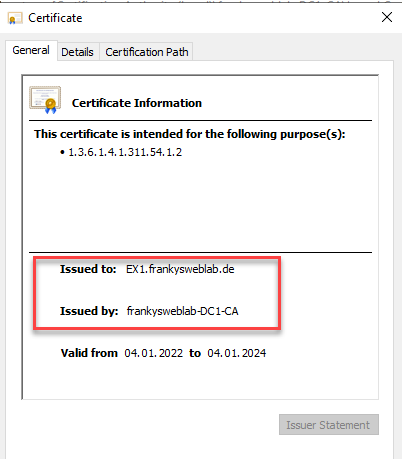
Nothing more needs to be done, it is only important that RDP connections are established with the FQDN (not with the UNC name), as only the FQDN is specified on the certificate:
Welchen Vorteil bietet denn das hier beschriebene RDP Zertifikat gegenüber dem ebenso automatisch ausgerollten Computer-Zertifikat mit gleicher Qualifikation? Mal davon abgesehen würde ich als Leser die OID „1.3.6.1.4.1.311.54.1.2„ gerne verstehen.
„ungenutzt“ ist relativ. Es wird sicher da ein oder andere mal vorkommen dass man auch auf einen Client per RDP muss. Wenn der ein passendes Zertifikat hat umso besser. Schaden kanns jedenfalls nicht.
Wenn das enrollment für „Domain Computer“ gesetzt ist, bekommen das Zertifikat aber auch alle Client-Geräte oder?
Könnte man das anders regeln, sodass nur Server das Zertifikat bekommen?
Deine Clients und deine Server sind hoffentlich nicht in der selben OU. Du setzt die GPO dann nur in der OU der Server ….würde ich vermuten.
Nein das natürlich nicht. Um die GPO mit Verwendung des RDP-Zertifikats gings mir auch gar nicht.
Es geht mir vielmehr um das Autoenrollment von Zertifikaten, welches bei uns sowohl für Server als auch Clients aktiv ist. Wenn das Zertifikatstemplate jetzt enrollment-Berechtigungen für „Domain Computer“ bekommt, dann landet das Zertifikat ja auch auf allen Clients. Es liegt dort dann ungenutzt rum, aber ist trotzdem keine gute Variante.
Wichtig hierbei: Das Template darf KEINE Leerzeichen im DisplayName haben, ansonsten wird das Zertifikat bei jedem Booten neu angefordert (Ist ein tolles Feature, wenn es für 2500 Clients ausgerollt wird…)
Das lernt man ja gleich am Anfang, dass man das identisch mit dem Vorlagennamen konfiguriert und Leerzeichen sind sowieso nie eine gute Idee bei sowas. ;)
Was genau meckert er denn an? :)
„Unbekannter Herausgeber“
Hm also ich bin jetzt kein Zertifikatsexpert aber vielleicht musst du die Zertifikatsstelle bei den Clients noch hinterlegen, damit Sie vertrauswürdig ist.
Unbekannter Herausgeber heißt aber afair, dass dein Client eben nicht der ausstellenden CA vertraut. Im Zweifel mach im Forum einfach mal einen Thread auf, da ist das einfacher als hier in den Kommentaren.
Ich habe jetzt herausgefunden, dass dies nur bei bereits gespeicherten RDP-Verbindungen passiert, nicht bei neuen. In der Registry habe ich aber keine gespeicherten Hashes gefunden. Merkwürdig.
Stehen die gespeicherten Verbindungen nicht im Password Safe von Windows? Ich mach das nie, deswegen nur eine Vermutung.
Der Server hat in meinem Fall das Zertifikat bekommen, allerdings beschwert sich der RDP Client immer noch über das nicht vertrauenswürdige Zertifikat.
Das Zertifikat im Store sieht gut aus. Root CA wird auch vertraut.
Dann noch Tipps von MS das Zertifikat per WMI oder Registry zu setzen versucht, leider ohne Erfolg.
Verbindung über FQDN.
Danke und Grüße,
MG
Wenn das enrollment per gpo wie oben beschrieben durchgeführt wird, ist das autoenrollment als Berechtigung nicht notwendig. Das gpo enrollment ist aber am Ende eigentlich nur ein fallback, wenn der zertifikatsregistrierungsagent nicht konfiguriert wurde. Das sollte man aber tun, sonst sammeln sich über die Jahre am Server die abgelaufenen Zertifikate. Das könnte der Agent sonst gleich mit aufräumen. ;)
Gibt es eine gute Anleitung, wie man einen Zertifikatsregistrierungsagent korrekt konfiguriert?
Naja soviel gibts da nicht zu konfigurieren. Im Zweifel mach bitte einen Thread im Forumsbereich auf, da kann man besser unterstützen (inkl. Screenshots).