This howto describes the installation of Exchange 2016 on Windows Server 2016.
Note: This article is a bit older. There is an updated version here:
Create Active Directory account
Windows Server 2016 relies on a stricter user separation. It is therefore not advisable to install the Exchange Server with the "Administrator" user; instead, an administrative user should be created to carry out the Exchange installation. This is not a service account with which the Exchange services are started.
The following rights are required for the account that performs the Exchange installation:
- Domain Admins
- Organization Admins
- Scheme admins
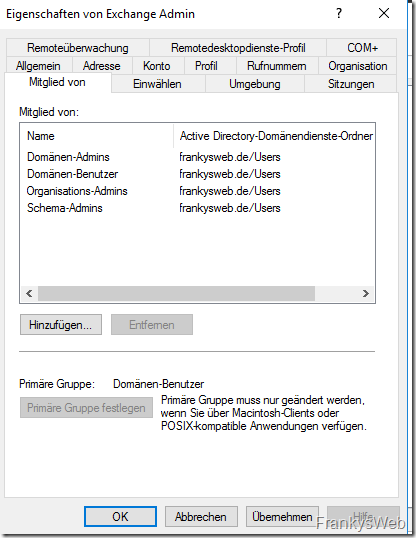
Note: The "Schema Admins" group is only required if the schema is extended during the Exchange installation. The schema can also be extended separately with another user before the Exchange installation.
Install prerequisites
The easiest way to install the required Windows features and roles is via PowerShell:
Install-WindowsFeature NET-WCF-HTTP-Activation45, RPC-over-HTTP-proxy, RSAT-Clustering, RSAT-Clustering-CmdInterface, RSAT-Clustering-Mgmt, RSAT-Clustering-PowerShell, Web-Mgmt-Console, WAS-Process-Model, Web-Asp-Net45, Web-Basic-Auth, Web-Client-Auth, Web-Digest-Auth, Web-Dir-Browsing, Web-Dyn-Compression, Web-Http-Errors, Web-Http-Logging, Web-Http-Redirect, Web-Http-Tracing, Web-ISAPI-Ext, Web-ISAPI-Filter, Web-Lgcy-Mgmt-Console, Web-Metabase, Web-Mgmt-Console, Web-Mgmt-Service, Web-Net-Ext45, Web-Request-Monitor, Web-Server, Web-Stat-Compression, Web-Static-Content, Web-Windows-Auth, Web-WMI, Windows-Identity-Foundation, RSAT-ADDS
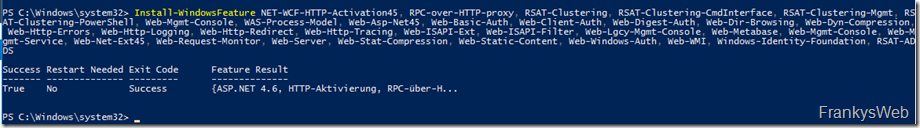
Note: The PowerShell must be executed with administrative rights:
After installing the Windows features, UCMA Runtime 4 must be installed:
Unified Communications Managed API 4.0 Runtime
Configure Windows Server
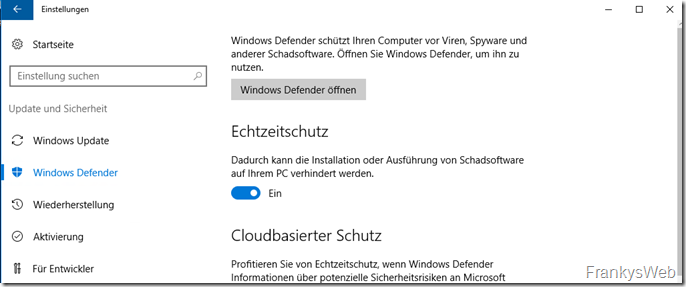
Windows Defender should be temporarily deactivated before the Exchange Server installation. Otherwise the installation may take longer and cause other problems:
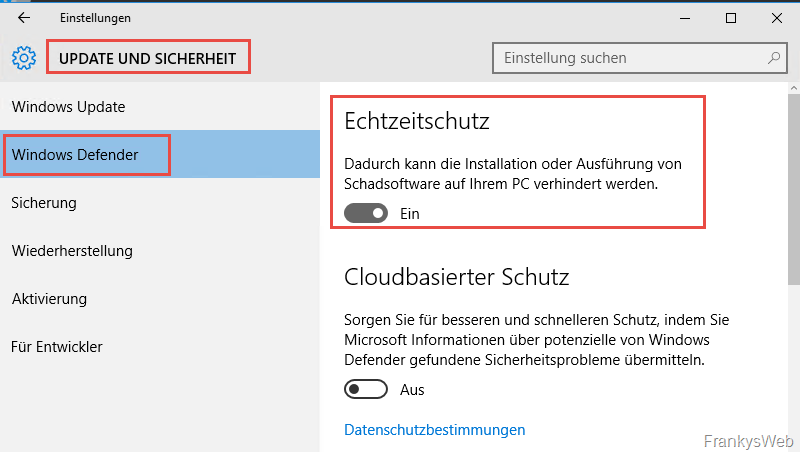
After the Exchange installation, Windows Defender is configured accordingly and switched on again.
General recommendation for Exchange Server: The size of the swap file should be set to the size of the RAM plus 10 MB. With 10 GB RAM (10240 MB + 10 MB), this results in a fixed swap file size of 10250 MB:
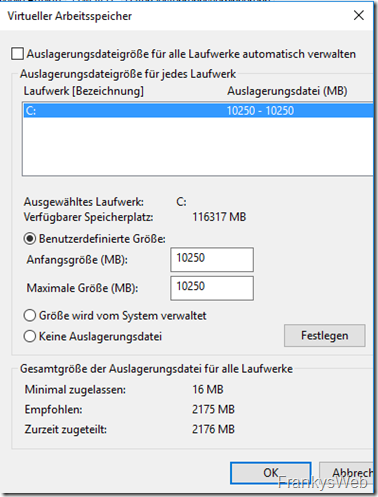
If the Exchange Server has 32 GB or more RAM, the maximum size for the swap file is 32778 MB. With 64 GB RAM, this remains at 32778 MB.
Furthermore, for performance reasons, the following assignment of drives is advisable:
- Laufwerk C:\ für die Windows Installation
- Laufwerk D:\ Auslagerungsdatei
- Laufwerk E:\ Exchange Installation
- Laufwerk F:\ Datenbank
- Laufwerk G:\ Logfiles der Datenbank
If you have several databases, it is advisable to mount the database and log files in folders so that you do not run out of drive letters.
Several SCSI controllers can also be used in virtual environments:
- SCSI Controller 1 for C:, D: and E:
- SCSI Controller 2 for F:
- SCSI Controller 3 for G:
Exchange Server Installation
Once the operating system has been prepared, Exchange Server 2016 can be installed. Windows Server 2016 is supported from Exchange 2016 CU3. The CU3 is also suitable for installation and can be downloaded here:
Cumulative Update 3 for Exchange Server 2016 (KB3152589)
The Exchange installation is then unspectacular, so I will only comment in the relevant places:
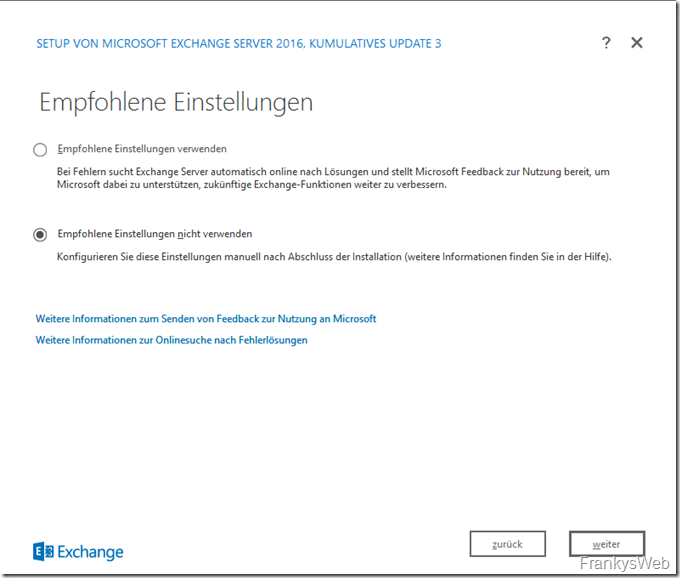
Following the license conditions, it is recommended to select "Do not use recommended settings", as otherwise settings will not be available in the further course:
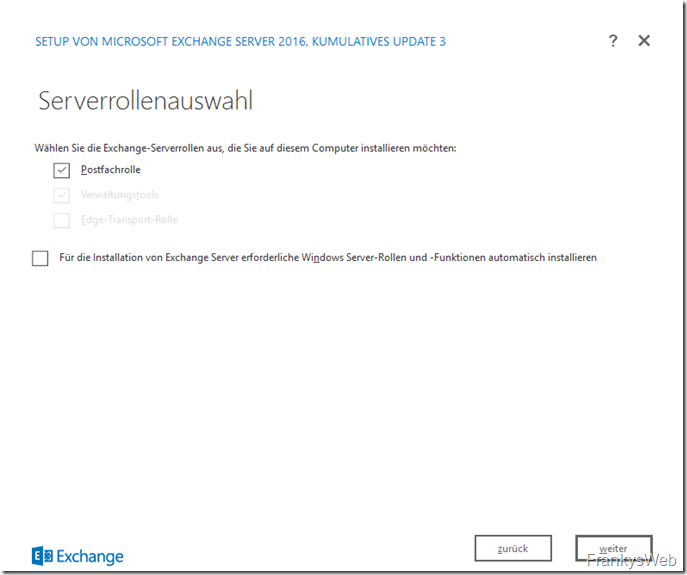
Exchange 2016 only has one role (mailbox role), apart from the Edge Transport role:
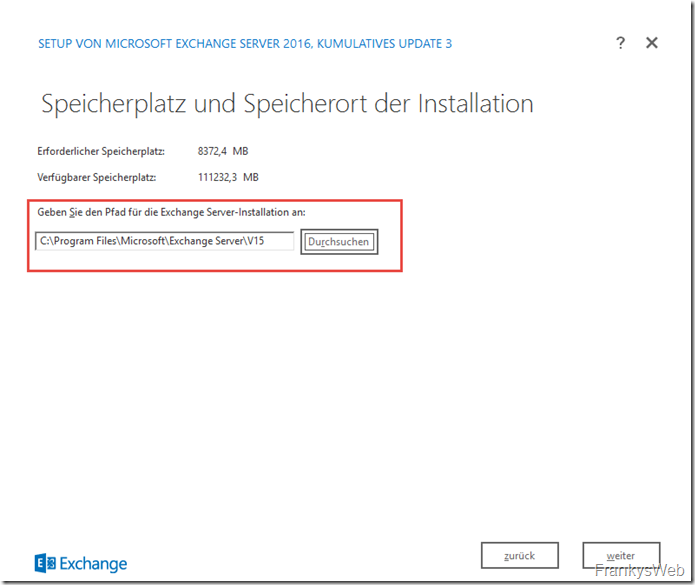
After selecting the mailbox role, the installation directory can be customized. As described above, the installation directory should be located on a separate partition or hard disk:
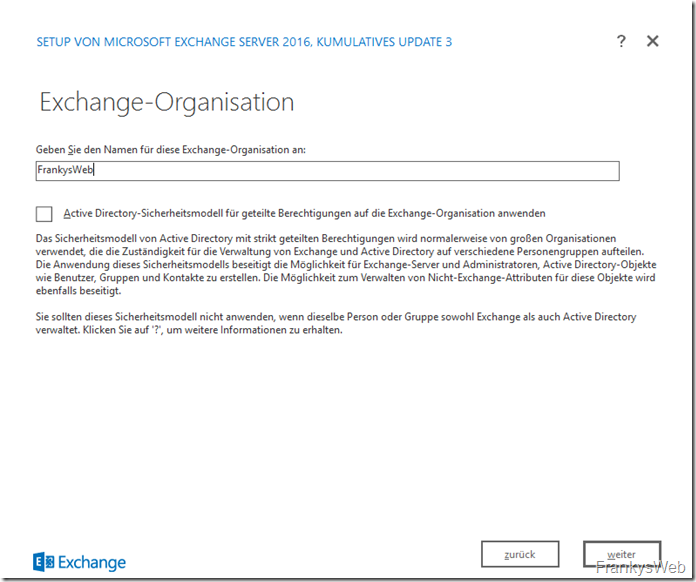
You can now enter the name of the Exchange organization:
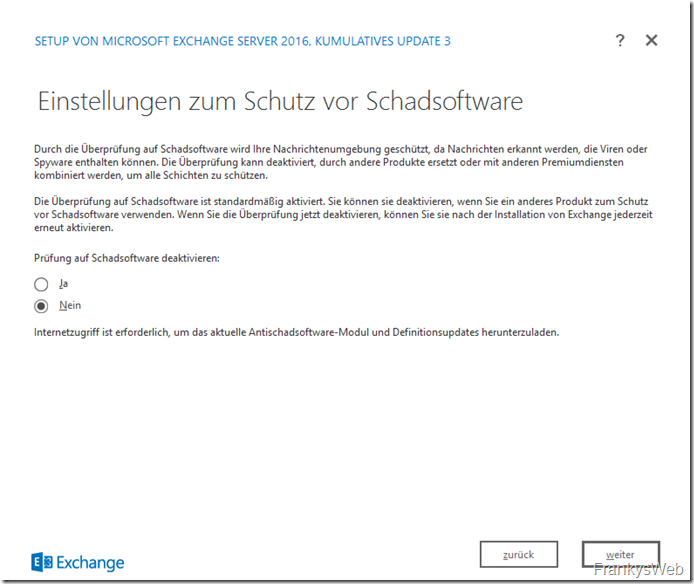
If all requirements are met, only the warning appears that the Active Directory schema will be extended if it has not been done before.
Once the installation is complete, Windows Defender can be configured.
Configure Windows Defender
Windows Defender is activated by default on Windows Server 2016. As Exchange Server requires some exclusions from the virus scanner, these must also be stored accordingly in Windows Defender. The same applies to virus scanners from other manufacturers.
The following information can be found on the Exchange Team Blog:
Windows Defender is on by default in Windows Server 2016. Attention to malware settings is particularly important with Exchange to avoid long processing times during installation and upgrade, as well as unexpected performance issues. The Exchange team recommends the Exchange installation and setup log folders be excluded from scanning in Windows Defender and other Anti-Virus software. Exchange noderunner processes should also be excluded from Windows Defender.
Source: Exchange Team Blog
The exclusions for Exchange 2016 are documented here in Technet:
However, the list is long, so Exchange MVP Paul Cunningham has published a script that clearly sorts the folders, processes and file types into 3 files. You can download the script here:
Generate Antivirus Exclusions for Exchange 2013 and 2016 Servers
To avoid having to enter all exclusions manually in Windows Defender, I have created a script that uses the files from Paul's script and adds the exclusions to Windows Defender via PowerShell:
Exchange 2016: Virus scanner exclusions (script for Windows Defender)
Once the exceptions have been entered, Windows Defender can be reactivated.
Note: This article is a bit older. There is an updated version here:
Hallo
ich habe versucht auf einem Server 2016 Standard ein Exchange 2016 Enterprise zu installieren
das Setup bricht ab, weil es noch einen Exchange 2000 oder 2003 finden würde – man muss diesen entfernen
Zu finden ist der ehemalige Server „swinger“ mittels Exchange Powershell auf dem Mailserver (Exchange 2010)
[PS] C:\Users\administrator.DOMAIN\Desktop>Get-ExchangeServer
Name Site ServerRole Edition AdminDisplayVersion
—- —- ———- ——- ——————-
SWINGER None Standard Version 6.5 (Bui…
EXCHANGE DOMAIN… Mailbox,… Enterprise Version 14.3 (Bu…
[PS] C:\Users\administrator.DOMAIN\Desktop>get-addomain |format-list name, domainmode
name : DOMAIN
domainmode : Windows2008R2Domain
Diesen „Swinger“ gab es, als ich entweder von EX 5.5 auf Ex 2000 oder aber vermutlich via EX 2007=SWINGER benannt auf EX 2010 wechselte.
Diesen Swinger gibt es nicht mehr:
Nicht im DNS, den Registries von Domainkontroller (Server 2016) oder dem Exchange 2010 auf Server 2008R2
IM ADSIedit kann ich nicht suchen, und bei manuellem Suchen ist sicherlich ein Übersehen möglich.
Wie kann ich auf dem Exchangeserver diesen EIntrag „Swinger“ mitteles Powershell gnadenlos entfernen?
Grüsse
Alex.
Hat sich erledigt dank der vielen versteckten Infos.
Solved.
Hallo
ich habe folgendes Problem:
Exchange 2016 auf ws 2016 und eigenen dc auf 2016.
hatte ne feste IP (zb 123.123.123.123)
nun wurde die ip vom Provider auf (zb 234.234.234.234)
geändert.
Exchange will nun Emails immer über 123 versenden was aber nicht geht . Empfangen geht auch nicht mehr obwohl die IP in der Domäne angelegt ist.
´Wie ändere ich nun die konfi ab das Exchange über 234. versendet?
2018-03-09T18:22:40.478Z,Eingehender Proxy: Interner Sendeconnector,08D580E857ED566C,2,,123.123.123.123:2525,*,,“Failed to connect. Winsock error code: 10060, Win32 error code: 10060, Destination domain: internalproxy, Error Message: Ein Verbindungsversuch ist fehlgeschlagen, da die Gegenstelle nach einer bestimmten Zeitspanne nicht richtig reagiert hat, oder die hergestellte Verbindung war fehlerhaft, da der verbundene Host nicht reagiert hat 123.123.123.123:2525.“
@Sven
Ich denke du nimmst die Installationsdatei mit ca. 1,6 GB, diese läuft auf Win Server 2016 (Ich gehe davon aus, dass du Win 2016 verwendest) nicht. Du musst dir ein CU herunterladen, CU7 (5,5GB) ist aktuell. Dann kommt die Meldung nicht bei der Installation
Kann mir jemand helfen? Ich stolpere immer wieder über folgenden Fehler ….
Die Windows-Komponente Server-Gui-Mgmt-Infra ist nicht auf diesem Computer installiert. Sie muss installiert werden, bevor das Exchange-Setup gestartet werden kann.
Hallo Zusammen,
bezüglich des Adminusers für die Installation: Löscht ihr diesen danach, oder lasst ihr ihn für das nächste CU im AD?
Vielen Dank und Grüße
Marco
Also bei mir ging es mit dem Admin Konto nicht.. Ich musste tatsächlich einen neuen Benutzer für Exchange Installation erstellen.
Was hat es denn genau mit der „strikteren Benutzertrennung“ auf sich? Habe den Admin bisher eigentlich immer genutzt da den keiner kennt und nutzt, außer halt wenn wirklich mal was administrativ gemacht werden muss.
Hallo :)
kann ich die Pfade
Laufwerk C:\ für die Windows Installation
Laufwerk D:\ Auslagerungsdatei
Laufwerk E:\ Exchange Installation
Laufwerk F:\ Datenbank
Laufwerk G:\ Logfiles der Datenbank
nachträglich noch ändern? Habe meine Exchange 2016 schon ein weilchen laufen…
Wenn ja wo?
Danke
Grüße
Hi,
der Pfad für die Windows Installation und die Exchange Installation lässt sich nachträglich nicht mehr ändern. Alle anderen Pfade kannst du entsprechend ändern.
Gruß, Frank
Ok, selbst schuld wenn man nicht richtig liest. Es ist ja 2016 CU3 nötig.
PS C:\Users\exchange> Install-WindowsFeature Server-Gui-Mgmt-Infra –Restart
Install-WindowsFeature : ArgumentNotValid: Die Rolle, der Rollendienst oder der
Featurename ist ungültig: „Server-Gui-Mgmt-Infra“. Der Name wurde nicht
gefunden.
In Zeile:1 Zeichen:1
+ Install-WindowsFeature Server-Gui-Mgmt-Infra –Restart
+ ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
+ CategoryInfo : InvalidArgument: (Server-Gui-Mgmt-Infra:String) [
Install-WindowsFeature], Exception
+ FullyQualifiedErrorId : NameDoesNotExist,Microsoft.Windows.ServerManager.
Commands.AddWindowsFeatureCommand
Success Restart Needed Exit Code Feature Result
——- ————– ——— ————–
False No InvalidArgs {}
nein. Mist, auch als anderer Benutzer doch der gleiche fehler
Hab den Fehler gefunden. Ich habe das setup als administrator gestartet.
Hallo
danke für deine Anleitung, aber auch nach Installation der Features per PS mit deinem Befehl meckert Exchange. Ich verstehe nicht was er hier noch benötigt. Jemand einen Tipp?
Fehler:
Die Windows-Komponente Server-Gui-Mgmt-Infra ist nicht auf diesem Computer installiert. Sie muss installiert werden, bevor das Exchange-Setup gestartet werden kann.
Weitere Informationen finden Sie unter: http://technet.microsoft.com/library(EXCHG.160)/ms.exch.setupreadiness.ServerGuiMgmtInfraNotInstalled.aspx
Hallo
Ich habe bereits Server 2016 und Exchange 2016cu3 am laufen. Mit Outlook 2013 funktioniert es wunderbar. Mit Outlook 2016 kommt immer dass Outlook nicht gestartet werden kann. Ordnergruppe etc kann nicht geöffnet werden. Kennt dieses Problem schon Jemand???
Gruss Michel
Hi,
Server 2016 und Exchange 2016 laufen bei mir bisher problemlos. Hast du mal geprüft ob die Authentifizierungsmethoden auf dem /mapi Verzeichnis im IIS passen?
Gruß, Frank
Gestern war ich bei MS in MUC … im vortrag wurde das neue robuste filesystem angesprochen … damit müsste es ruckizuki gehen … hat das schon jmd ausprobiert?
Hi Carsten,
ja, allerdings bisher erst mit Server 2012 R2:
https://www.frankysweb.de/exchange-2016-storage-performance-mit-jetstress-testen-vergleich-ntfs-zu-refs-teil-1/
Einen neuen Test mit Server 2016 und Exchange 2016 bereite ich bereits vor.
Gruß, Frank
Mich würde es freuen, Exchange mal nicht auf einem Full Server System installiert werden muss, sondern eventuell auf einem Nano oder GUI freien System….
Auf dem Nano Server wird es wohl in absehbarer Zeit nicht laufen. :-)
Hi,
ein paar Frage habe ich.
1. Welche Größen empfehlen sich denn für die Partitionen „Betriebssystem“ und „Exchange“ Installation?
2. Die Logs vom Exchange sind dann auf der Exchange Installationspartition richtig ?
3. empfiehlt sich in einer virtuellen Umgebung überhaupt die Trennung von Betriebssystem und Auslagerungsdatei?
Vielen Dank
Gruß Björn
Hi,
zu 1) Die Größen hängen natürlich etwas von der Umgebung ab. Ich würde hier mit min. 50 GB für das OS und min. 100 GB für Exchange starten. Wenn es eine VM ist, lässt sich das ja schnell anpassen, sollte es mal knapp werden.
zu 2) Ja, lässt sich aber natürlich auch anpassen, per Default liegt das IIS Log Verzeichnis auf C:\, das sollte in jedem Fall angepasst werden
zu 3) Ja, allerdings ist auch das abhängig von der Umgebung. Das Gast-OS kann pro Disk eine IO-Queue starten, mehr Disks (auch VM-Disks) bedeuten mehr Queues, was in Engpass Situationen vorteilhaft sein kann.
Gruß, Frank